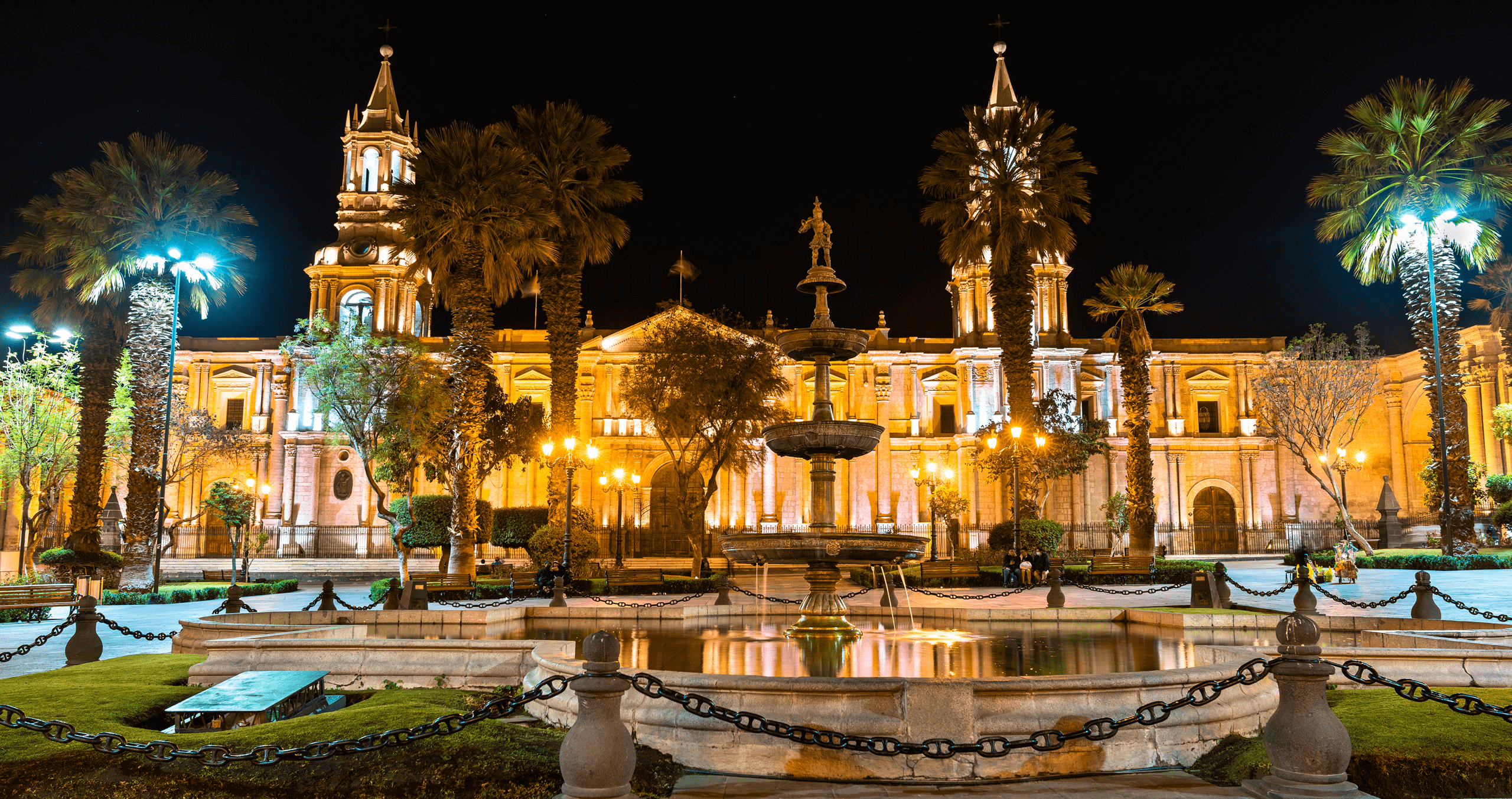

AREQUIPA
History
Its name is derived from the Queshwa word “ari-que pay”, meaning, “Yes, stay here” Arequipa is located at the division point between the central Andy region and the central-south Andy region, incorporating the valleys, which are located south of the Sihuas River. The division was more pronounced during the reign of the Wari Empire, which occupied the northern valleys up to the Sihuas River.
The cultural height coincides with the reign of the Churajon , which extensively occupied the Arequipa valleys, with densely inhabited villages and big agricultural projects that comprised irrigation projects, terraces and completely dominated valleys. In Arequipa there are important areas like Casapatac, Sabandia or Churajon, which are densely populated. En los valles del norte se desarrolló,en la misma época que Churajón, la Cultura Chuquibamba, con extensiones en las provincias sureñas de Ayacucho y con contactos con el Cusco.
The settlements of this culture, generally identified with the Collaguas, are especially notable in the Colca Valley. . Through Arequipa, the Incas descended to the Yunga region in search of new conquests. On the slopes of the Misti Volcano, the Spanish conquistadors led by Manuel de Carbajal founded the city of Arequipa.
In the Republican era, memorable revolutions took place here, such as those of Ramón Castilla, Mariano Prado, Nicolás de Piérola, Sánchez Cerro and others by those who have been called “caudillos colectivos” (collective leaders). Arequipa has become the center of the economic complex of southern Peru and is one of the most important milk producing departments of the country.
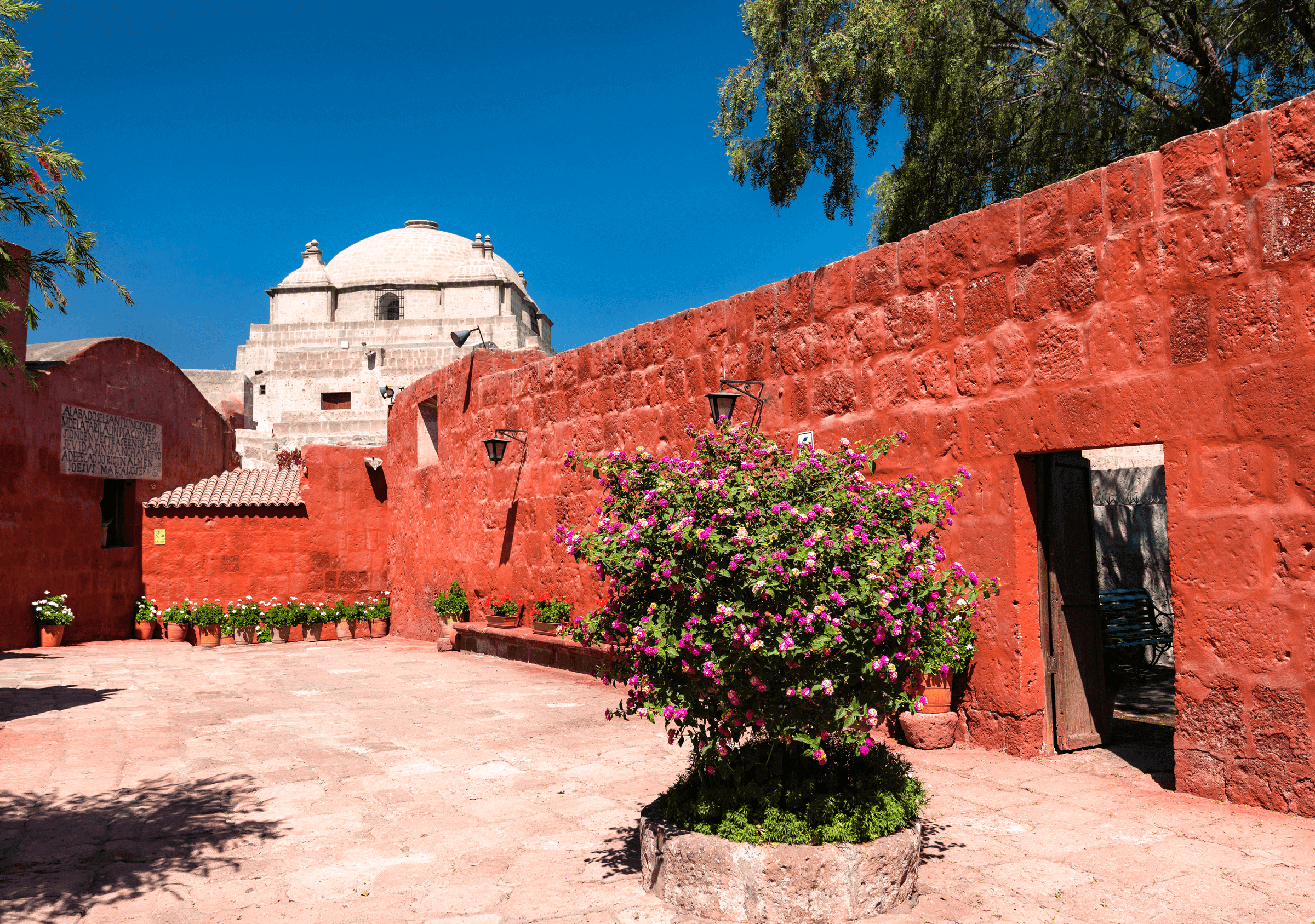
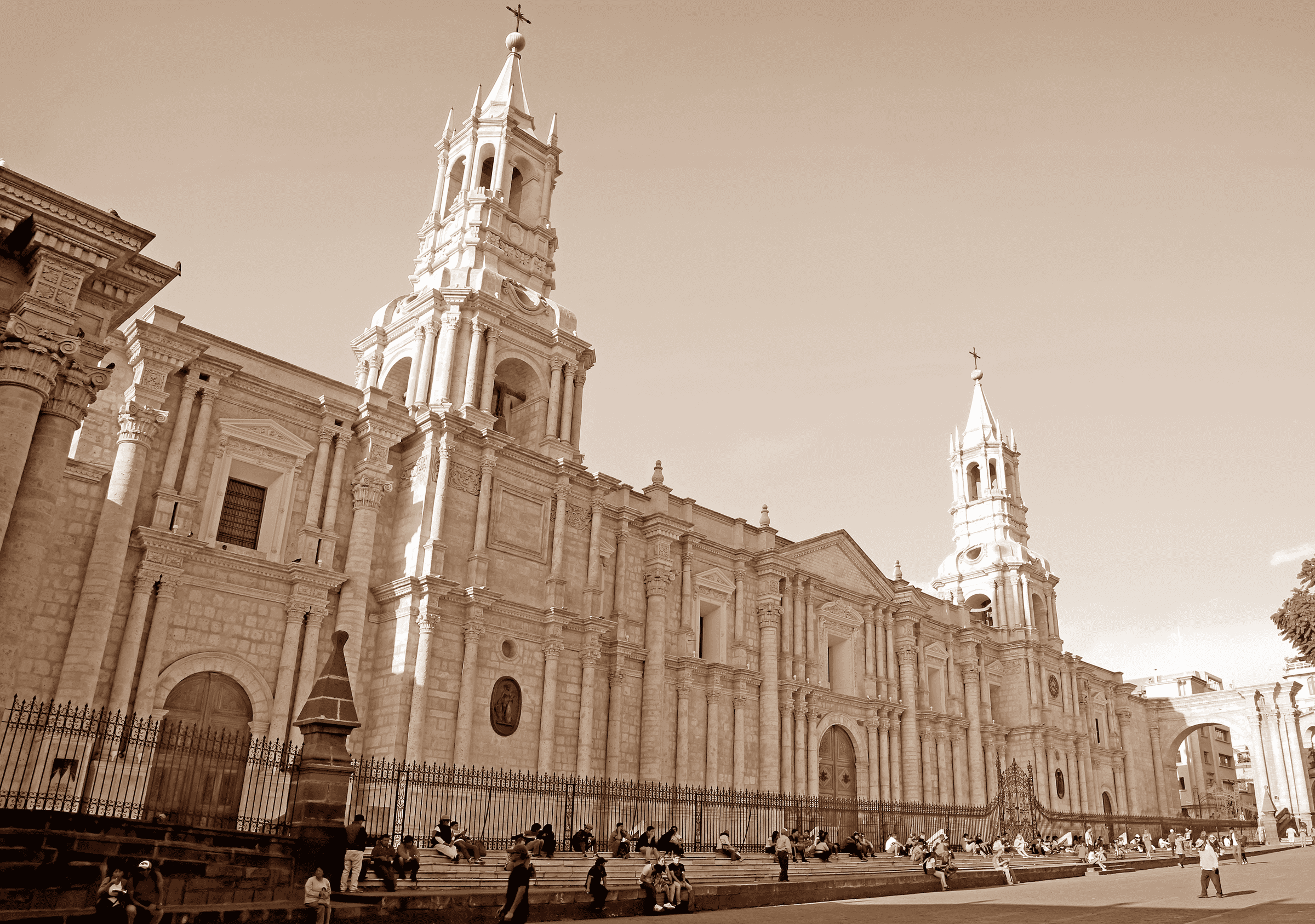
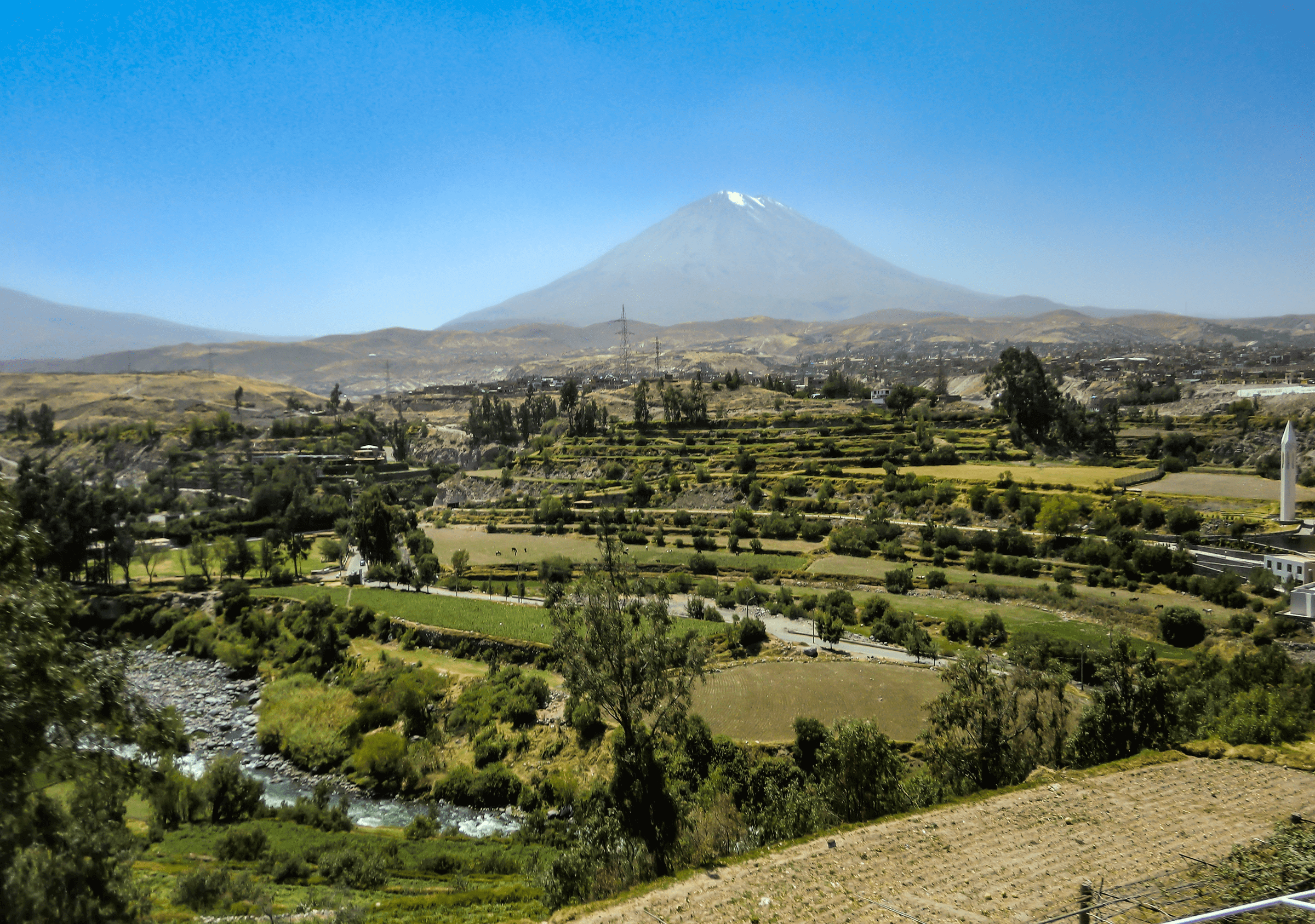



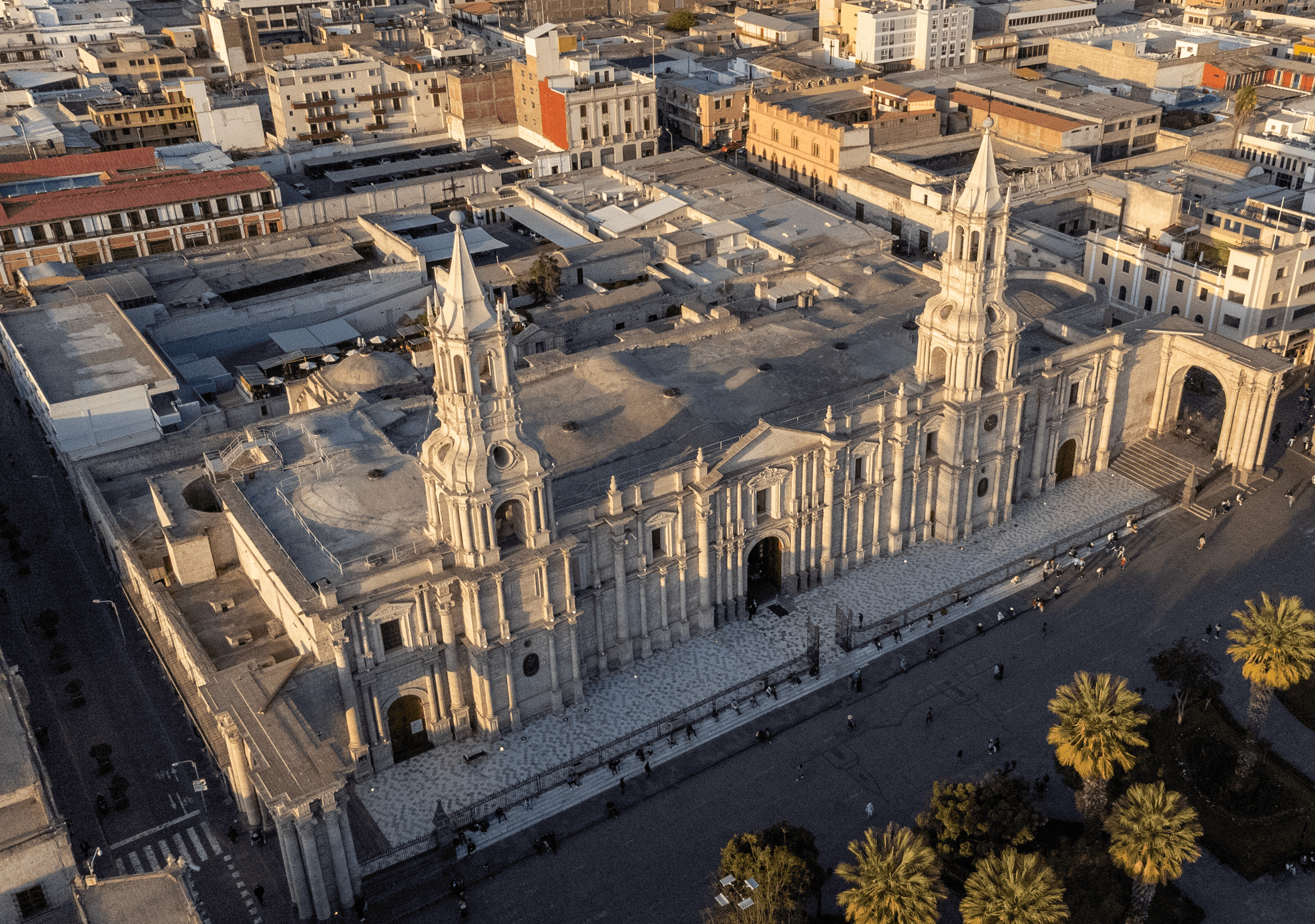
Geography
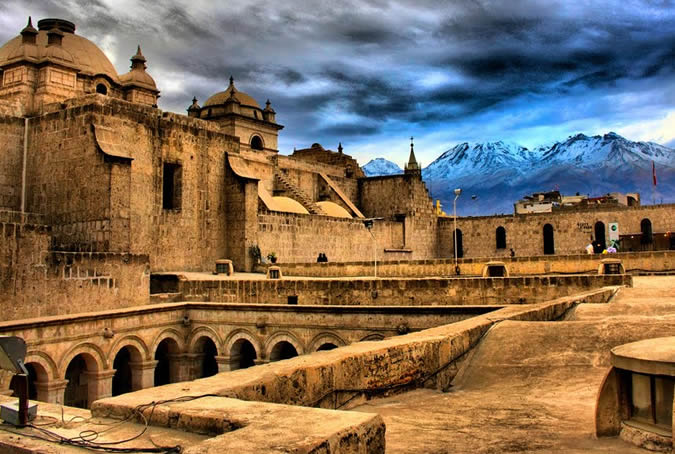
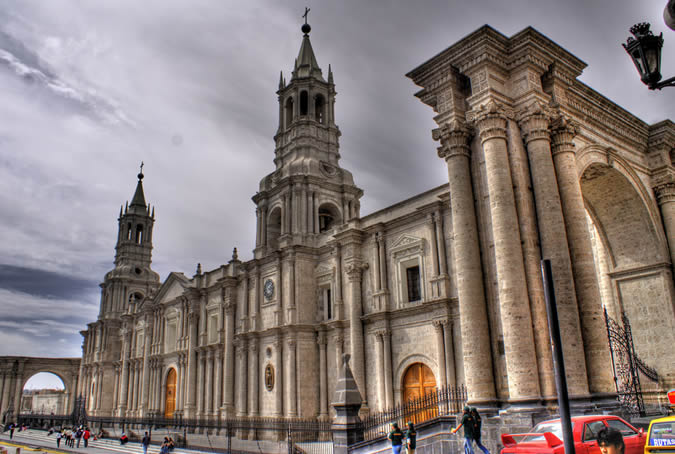
Tourism
Its contrasting background is the beautiful and imposing Misti Volcano. Besides, we can find beautiful beaches like Mejia, Mollendo and Camana, and thermo-medicinal baths like Yura, Socosani and Jesus.
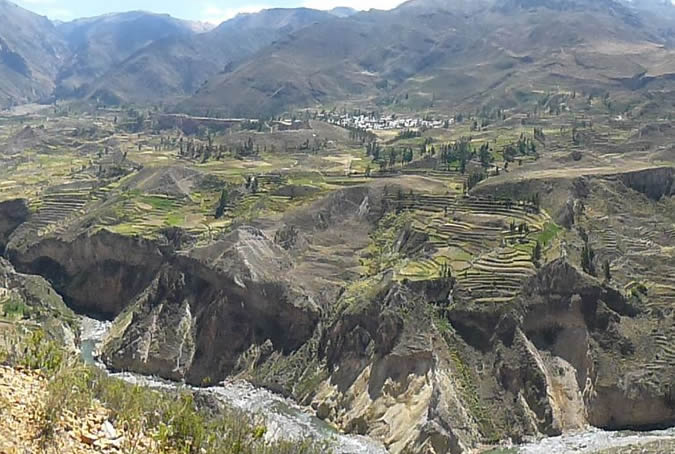
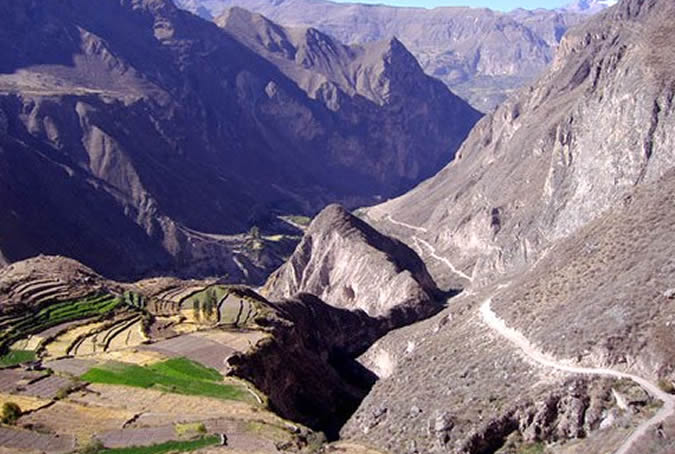
The Colca Canyon, which is located in the Province of Caylloma, is more than 100 km long and its deepest end starts a few kilometers after Chivay, its deepest point being 3,400mts. It is considered the deepest in the world. The area surrounding the Colca is considered to be very appropriate for practicing adventure tourism.(canoeing, rowing and hiking)
. The Aguada Blanca Reserve is one of the most important reserves for the reproduction of vicuña, a type of small llama-like animal that produces the finest wool for materials of the highest quality.
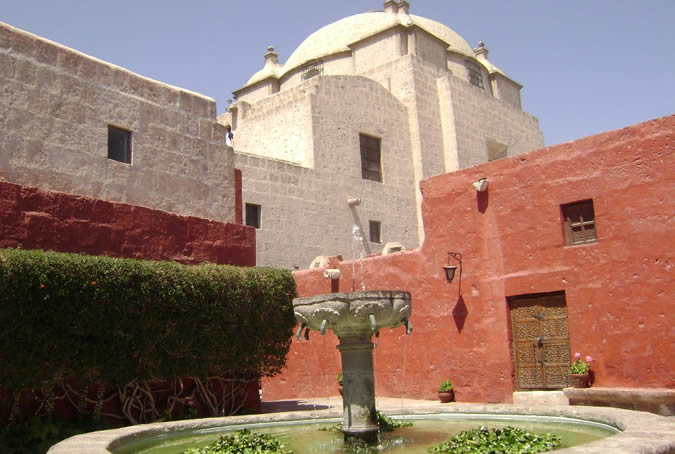
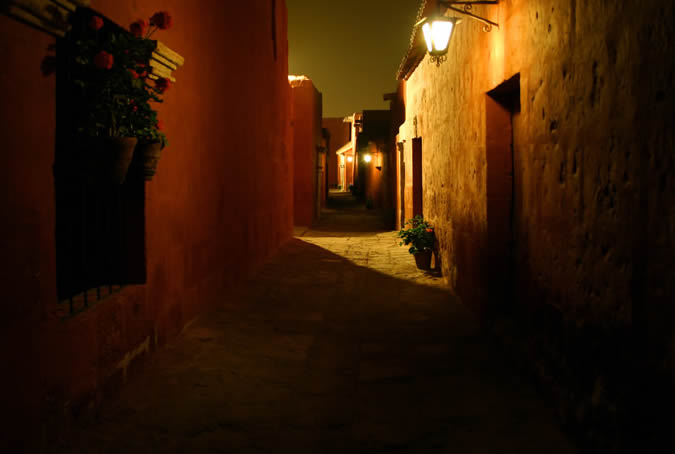
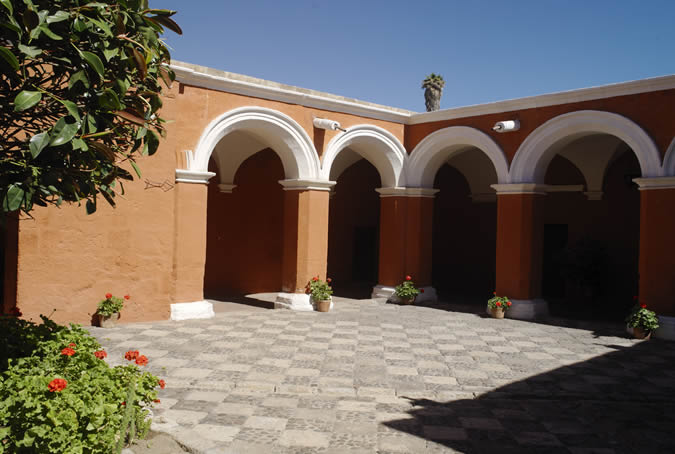
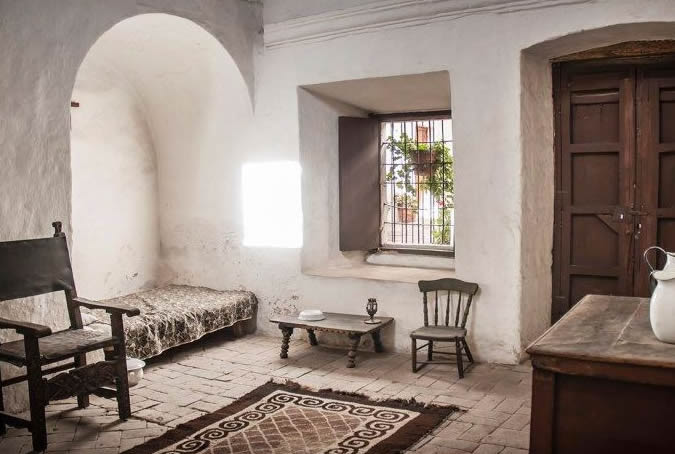
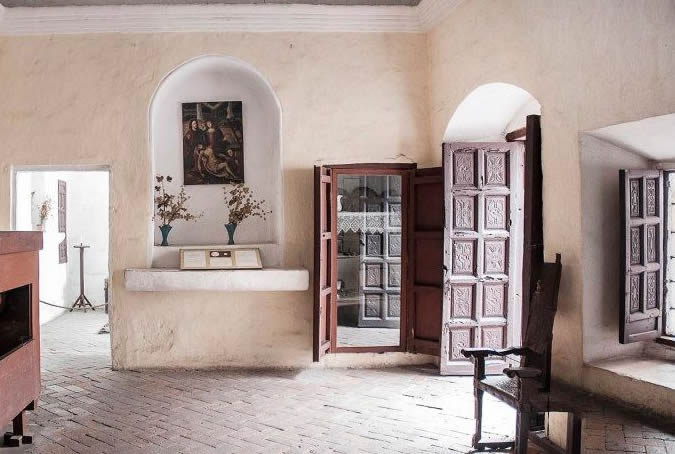
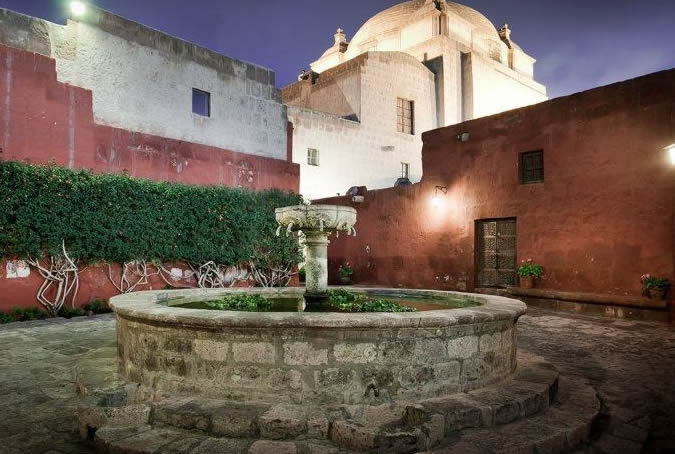
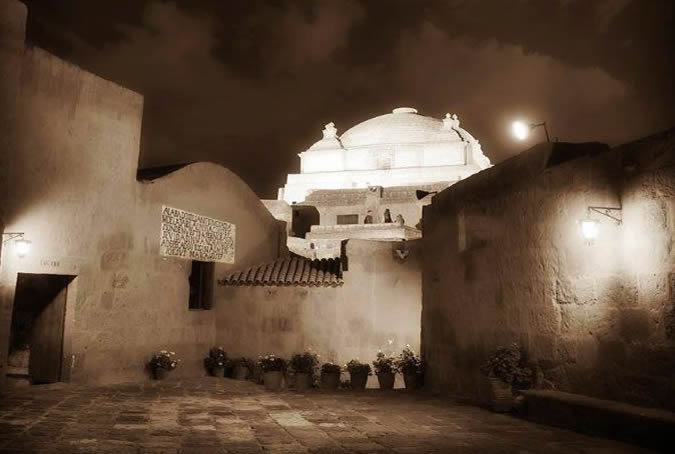
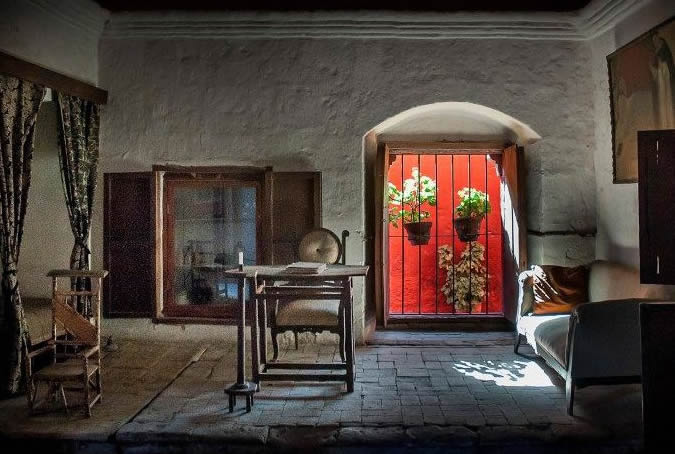
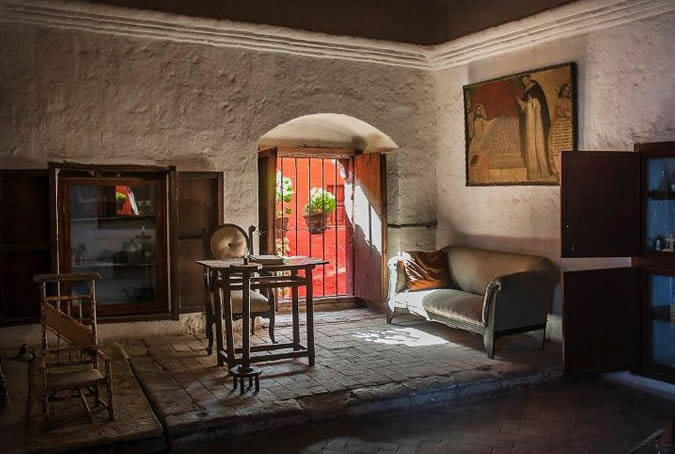
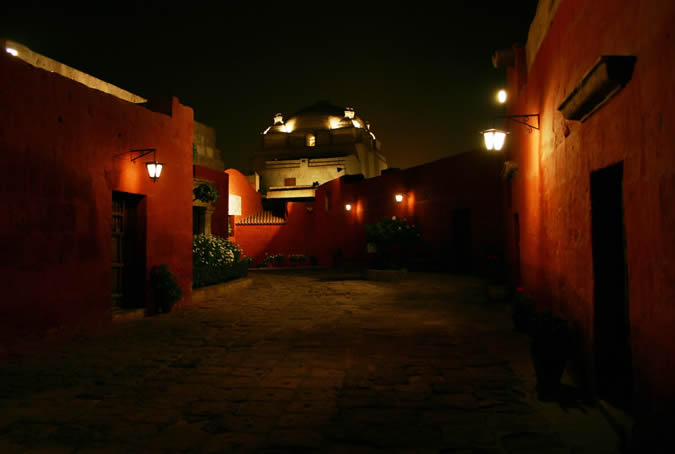
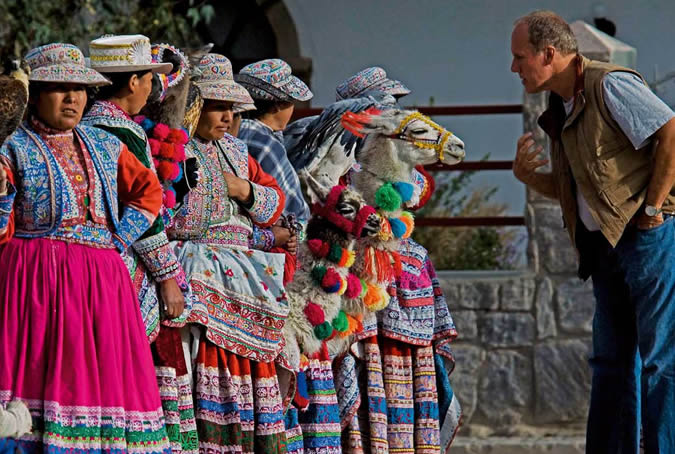
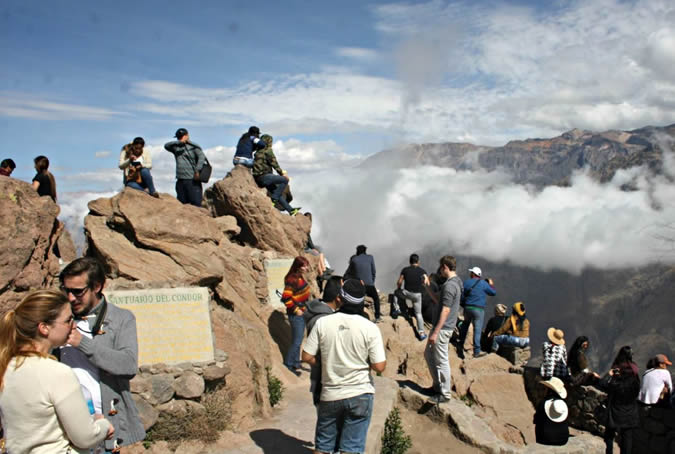
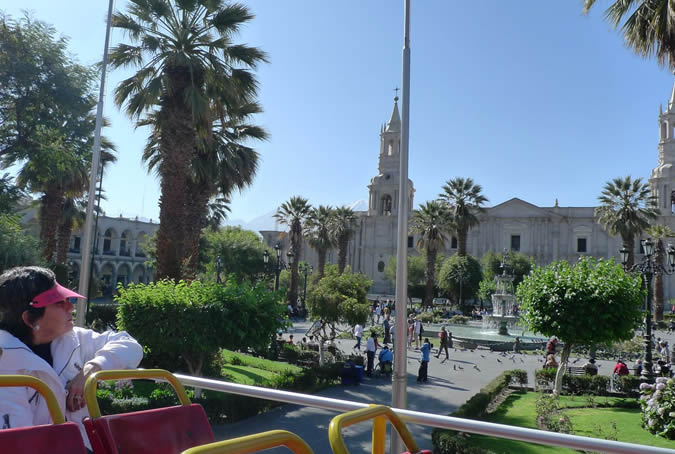
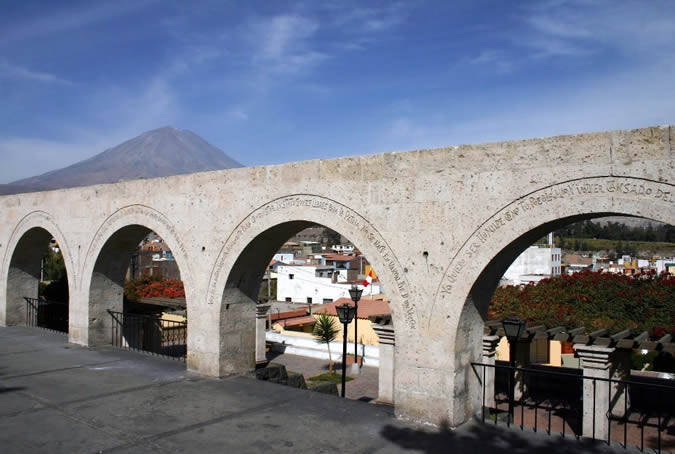
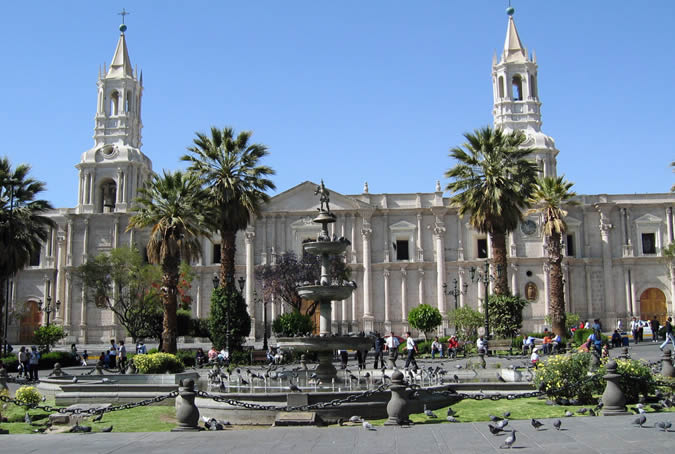
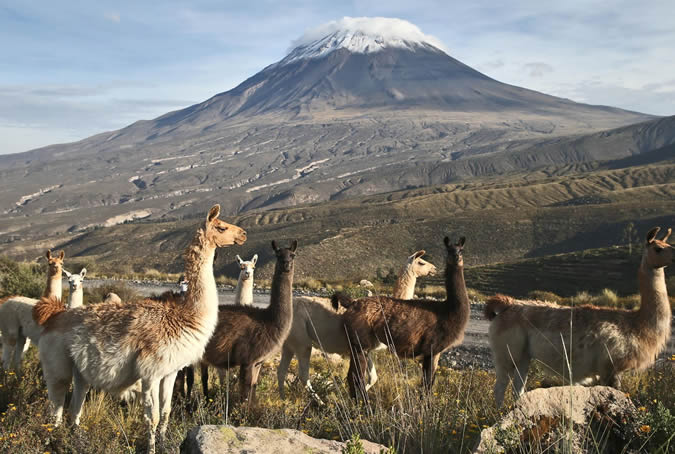



























Customs
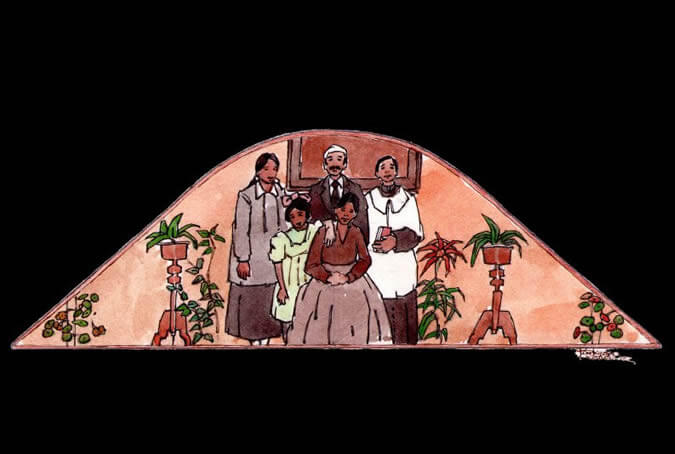

The typical Arequipenean family
The typical Arequipenean family
During colonial times, typical aristocratic families in the city lived in two or three-patio, majestic colonial homes called casonas - like the one you are currently visiting. Some traits these families shared were the numerous children and relatives they consisted of and the fact that they were devoutly Catholic and traditionalistic in their values and in their marked Spanish-heritage customs. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos
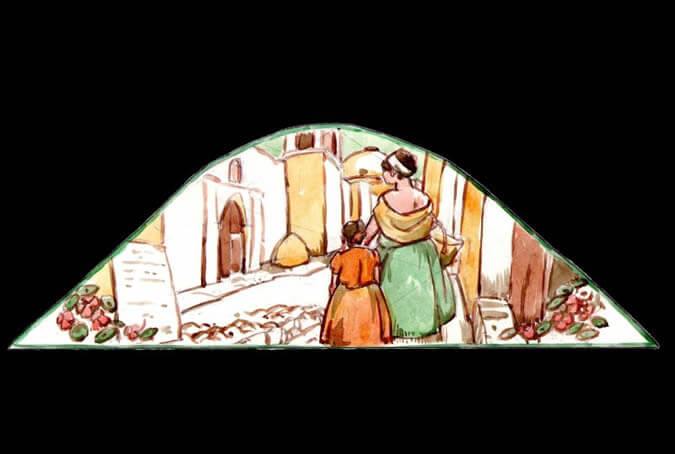

Family customs
Family customs
Every aristocratic Arequipenean family had among its children one male who wore a cassock and preached Christ's word, and one female who beginning in early childhood, regularly visited the Santa Catalina monastery to later wear a habit and serve the Lord. This daughter mortified her body to perfect her soul and spent countless hours of her life praying for the souls that she would help free from Purgatory. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos
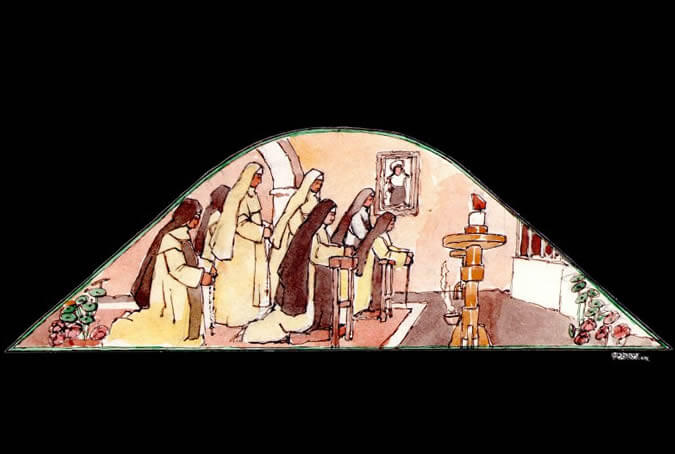

Nuns singing or praying
Nuns singing or praying
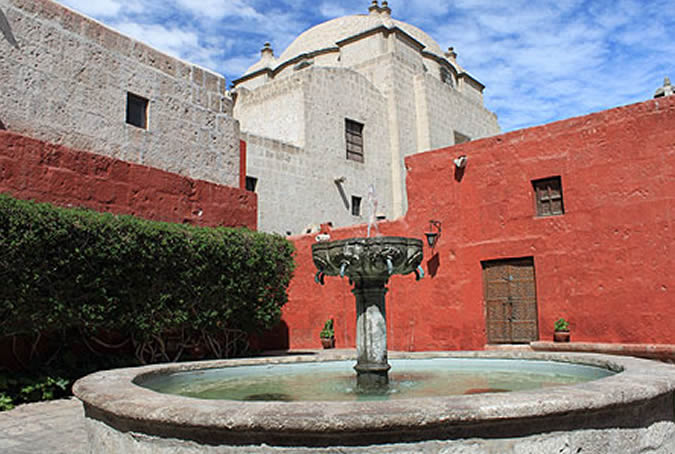
The prestige of this Dominican retreat house was recognized during the Peruvian viceroyalty. It was for this reason that throughout the history of the institution, among the nuns of the Santo Domingo de Guzmán order were some who came from Madrid, Barcelona and Seville, as well as others from Lima, Cuzco, the Colca Valley, La Paz and Oruro. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos!
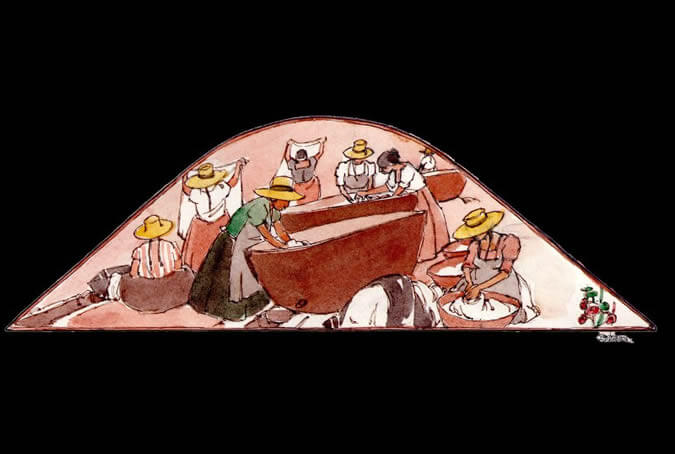

In the laundry room, maids washing table cloths
In the laundry room, maids washing table cloths
The nuns entered the Monastery with a dowry of treasures like furniture, utensils, etc. They also brought their own maids, whose task was to perform daily chores such as the laundry, the ironing, the cooking, and the cleaning, in this way allowing the religious women to devote all their time and strength to serving God. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos
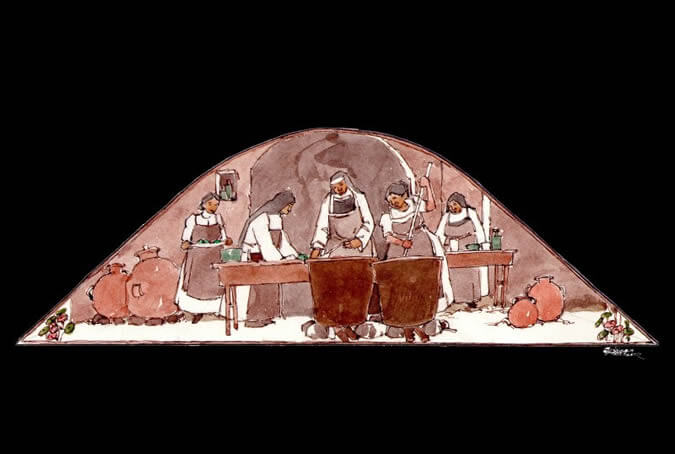
Making soap and perfumes
Making soap and perfumes
Some days, the nuns worked together in the elaboration of perfumes made of flower petals from the gardens of the Monastery. The essences were destined to perfume the cloths used on the church altars, the monasteries and the oratories in every cell. They also made parsley soap with a secret recipe which is safely guarded to this day and which is still prepared as treatment for wrinkles and rough skin. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos!
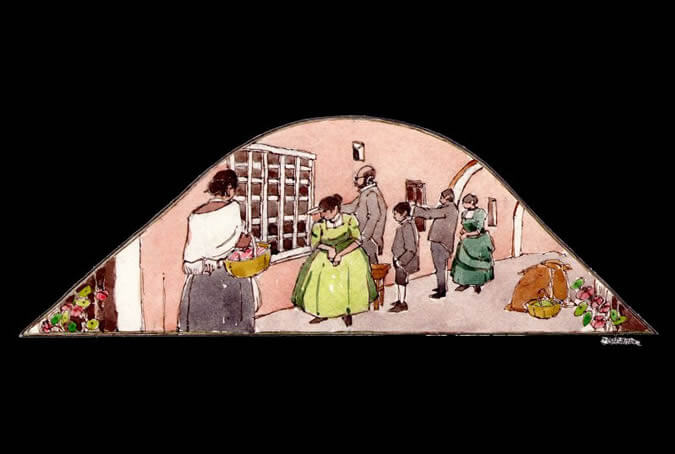

Family visits
Family visits
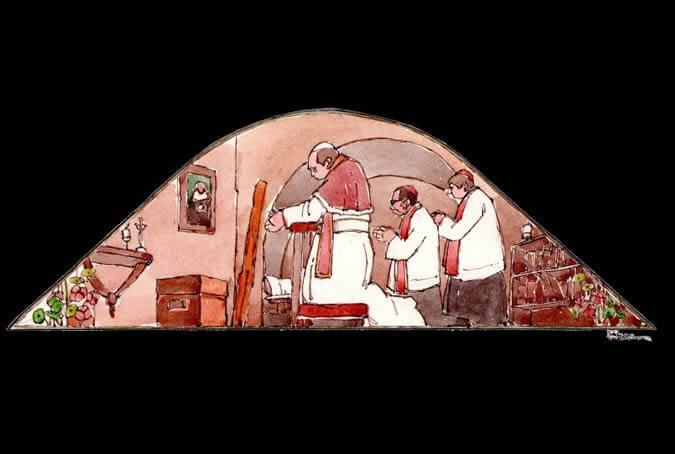
Given the religious life's demand for retreat from the outside world into a sacred feminine space, family members who wanted to visit their relatives in seclusion could only do so one day a week and by communicating through the visiting rooms for only a few minutes and only regarding the essential topics. The torno, a type of revolving dumbwaiter, was used to deliver supplies or written prayer petitions for the soul of an ill or deceased individual. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos!
The beatification of Sister Ana de los Angeles
The beatification of Sister Ana de los Angeles
Throughout the 16th century, Sister Ana de los Angeles Monteagudo lived in the Santa Catalina Monastery. She was a Dominican nun who led an exemplary life serving God and amazing the population with her gifts for premonition, bilocation and levitation. Upon her death, the beatification process began the first part of which culminated on the 2nd of February1985, when His Holiness John Paul II arrived in Arequipa for such purpose. Currently, the process is nearing its end and Sister Ana is soon expected to rise to the altars of sainthood. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos!
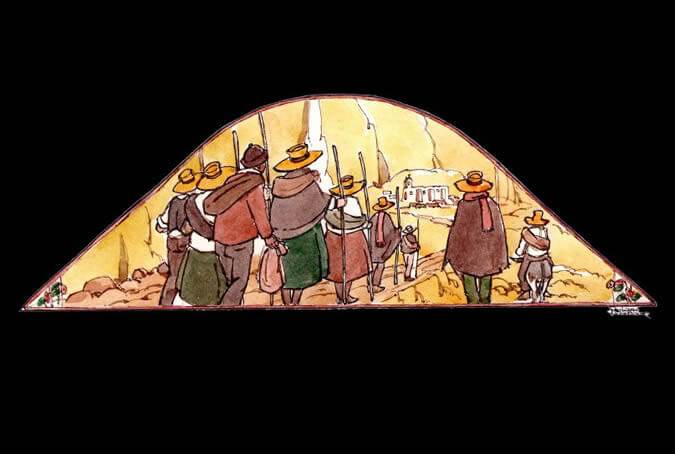

Peregrination to the Chapi sanctuary
Peregrination to the Chapi sanctuary
Since the beginnings of the 20th century, popular devotion to the Candelaria virgin - also called Purificación (Purification) or Presentación (Presentation) - has increased due to numerous peregrinations. On certain occasions such icons was named after specific places, which is the case with the Virgen de Chapi, whose worship goes back to the 16th century and who was first brought to the city in 1984 with a view to placate a drought that was affecting the region. It was transported via helicopter to Arequipa and after a service at the Cathedral, the Mamita de Chapi (Mommy from Chapi), as she is also known, fulfilled the awaited miracle, bringing with it the rain and putting an end to the drought. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos
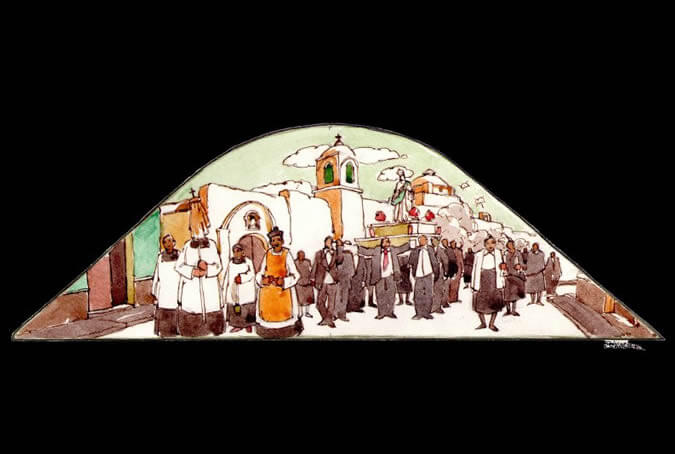

A procession with the Virgin Assumption
A procession with the Virgin Assumption
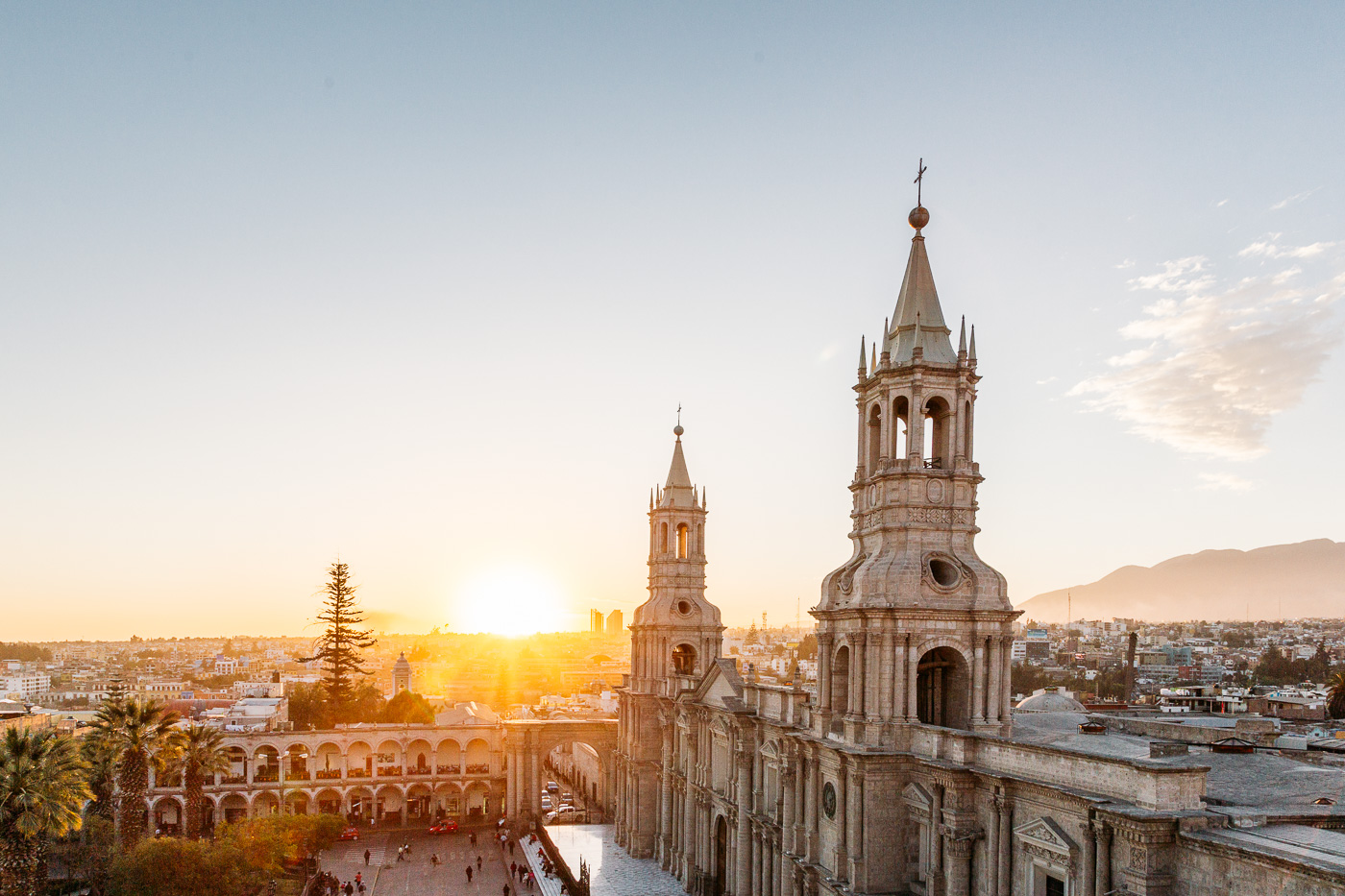
The city of Arequipa was founded by the Spanish on the 15th of August 1540, and it was called Villa Hermosa de Nuestra Señora de la Asunción (Beautiful Village of Our Lady of the Assumption). With that name, the population would remain under the advocacy of the Virgin Mary as its protector from all the misfortunes which might fall upon the inhabitants of the region. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos
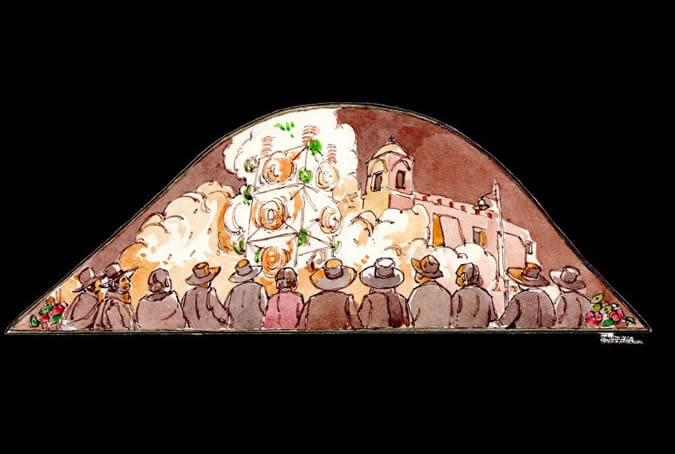

Fireworks
Fireworks
Traditionally, on the eve of every religious festivity, the capo entrance - bonfire wood - was brought in. The brotherhoods assumed the expenses of setting up the lavish fireworks made with reed towers decked with multi-colored lights which highlighted the traditional art of Arequipenean pyrotechnicians. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos
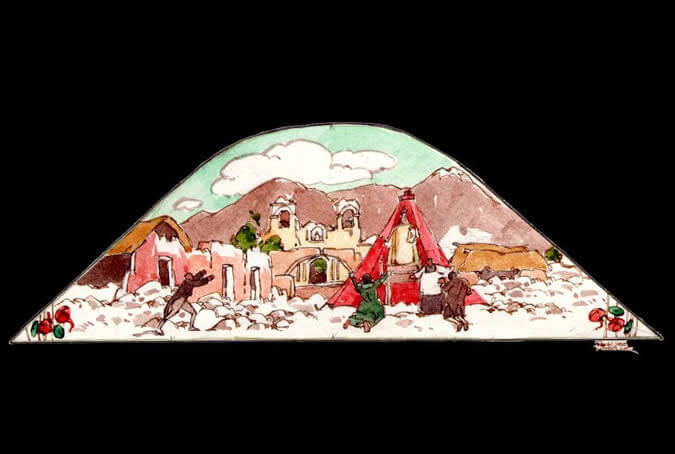

Earthquakes
Earthquakes
A dozen earthquakes destroyed part of the city, leaving it in ruins that were soon rebuilt by the local residents. The most devastating earthquake occurred in February 1600, when the Huaynaputina volcano - Putina the Young - erupted, causing two quakes and an ash cloud that fell upon the city for fifteen consecutive days in the most destructive natural disaster the Andean South had ever seen. The inhabitants took it as God's punishment for the sins both the whites and the indigenous people committed. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos
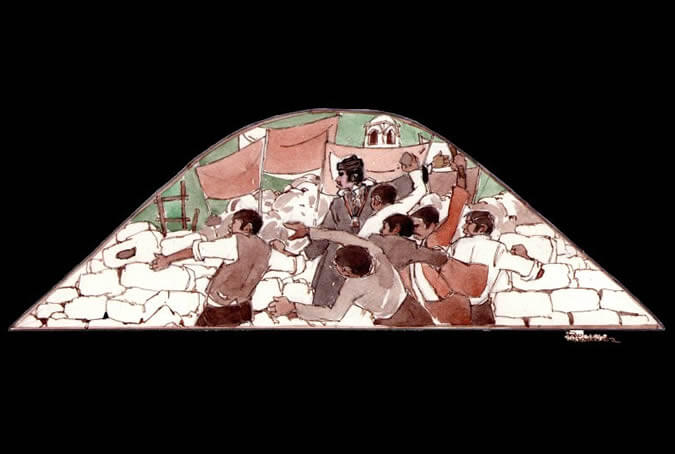

A revolution, an agitated people
A revolution, an agitated people
One of the roots of the Arequipenean idiosyncrasy took shape in the 19th century as the Arequipeneans became courageous and combative in street demonstrations and barricades. It was a religious man, Juan Gualberto Valdivia Cornejo (Dean Valdivia), who started and led the revolution against government abuse and centralism which would forever mark the Arequipenean people. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos
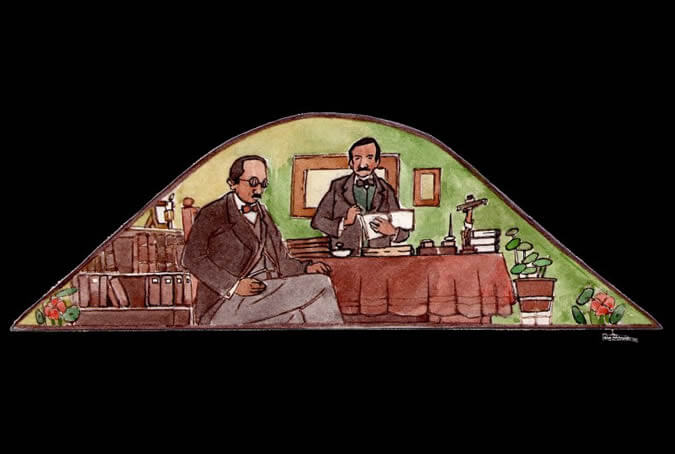

Arequipa, the cradle of law
Arequipa, the cradle of law
Our city has had among its illustrious citizens numerous scientists, writers and politicians, two of the most outstanding being Víctor Andrés Belaunde and José Luis Bustamante y Rivero. Both of these eminent men contributed to Peruvian and international law and coined the term peruanidad (Peruvianness), defined as the loving feeling that each one of us has for our beloved country. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos
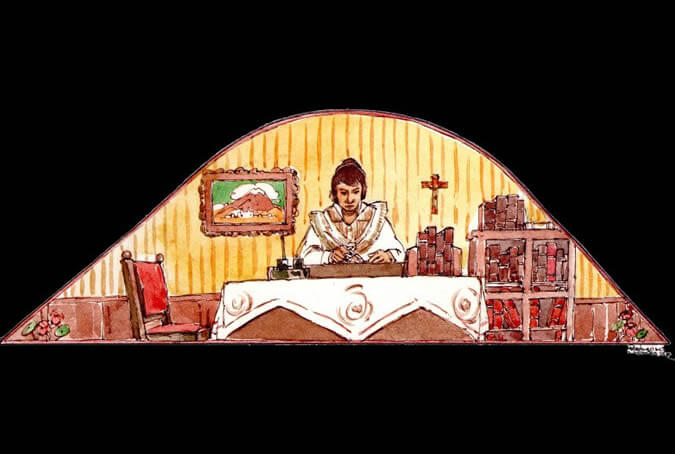

María Nieves y Bustamante
María Nieves y Bustamante
The most important Arequipenean female writer was Maria Nieves y Bustamante, who published Jorge o el Hijo del Pueblo (Jorge or the People's Son). This novel portrays an end-of-the-20th century romance between a humble and attractive young woman from Yanahuara and a wealthy young man from the city. The man soon forgets both the woman and the child they had together. Maria Nieves, with unquestionable modesty pointed out: I've only desired to be my people's mirror. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos
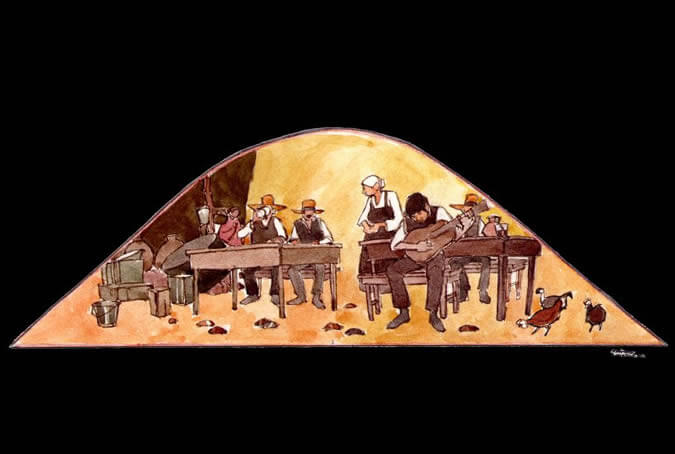

Arequipa, birthplace of yaravi
Arequipa, birthplace of yaravi
Yaravi, from arawi or jarawi, a sorrowful and melancholy Incan song, is a descendant of mixed race with Spanish elements such as the language (the local dialect) and the use of a guitar. This one-of-a-kind musical genre is most brilliantly represented by Mariano Melgar, a composer and interpreter who performed at the chicherias (bars where chicha, a type of corn beer was sold and consumed) and who was also a hero of the Peruvian independence and of the Arequipenean youth. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos
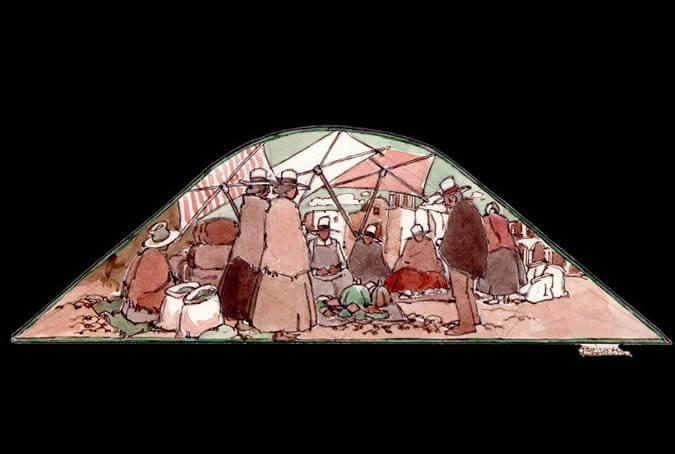

The main square market
The main square market
The heart of the city has always been the main square. In it, the royal, revolutionary and national troops were formed, and it is and has always been the setting for processions, parades, rows and exhibitions of all kinds. It was also the city's market and to it arrived countless products from the fields of the Chili river valley, Vitor, Majes and Siguas, which would be consumed on the tables of the various neighborhoods of the city. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos
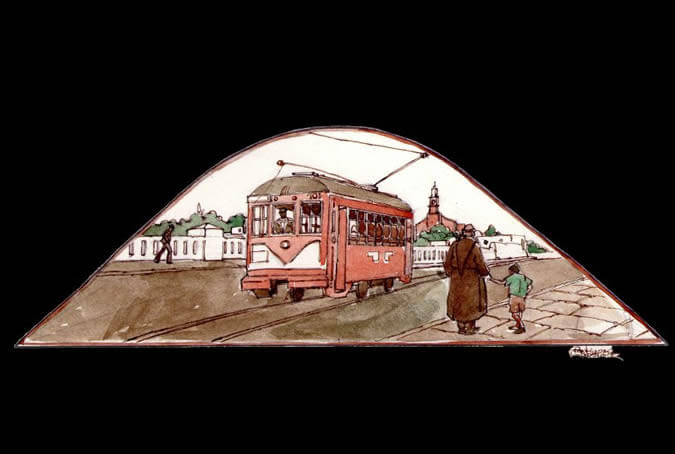

The streetcar crosses the Grau bridge
The streetcar crosses the Grau bridge
In the last third of the 19th century, the second bridge of the city was built, linking the San Lazaro neighborhood and Yanahuara, near the convent of the Recoleta Franciscana (Franciscan Convent). It was called the new bridge and following the Pacific War it was named after the national hero Miguel Grau, the Caballero de los Mares (Knight of the Seas). Years later, a streetcar regularly crossed the bridge transporting both the ccala people (from the city) and the loncca people, who were the farmers from the surrounding areas. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos
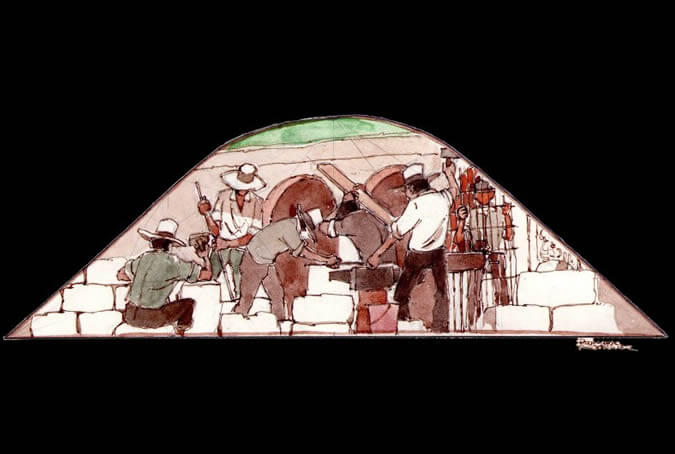
Cutting sillar (ashlar) and working iron
Cutting sillar (ashlar) and working iron
The volcanic stone from the ravines and quarries known as sillar was used, after the arrival of the Spanish, for door and window frames, for facades and for government, religious and secular buildings that still exist today. Sillar, moldable and cut by Indians from the area, harmonized well with the wrought iron of fences, doors, windows, lanterns, hinges and locks, creating a perfect union of traditionally Arequipenean architectural elements. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos
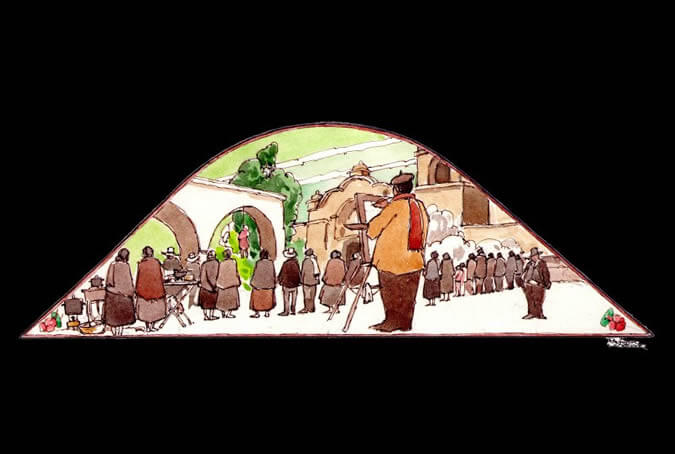

An artista at painting
An artista at painting
The landscape of the Arequipenean countryside, the churches, the convents, the streets of the city and of the nearby towns, the picanterias (typical restaurants), the riots, and the varied scenes of everyday Arequipenean life, have all been subjects for local painters (very prestigious nation-wide). These artists, many of them self-taught or educated in the Augustine cloisters, have stood out in a number of techniques and media. Painter: + Mr. José Luis Pantigoso Rodríguez Historian: Mr. Alejandro Málaga Núñez-Zeballos.


